Materials Chemistry |
please flag with care:
| |
| 2007-12-10 | No history |  | Add My version | |
download mind map 104435513.cdmm (mindmap file created by ConceptDraw MINDMAP)
| | |
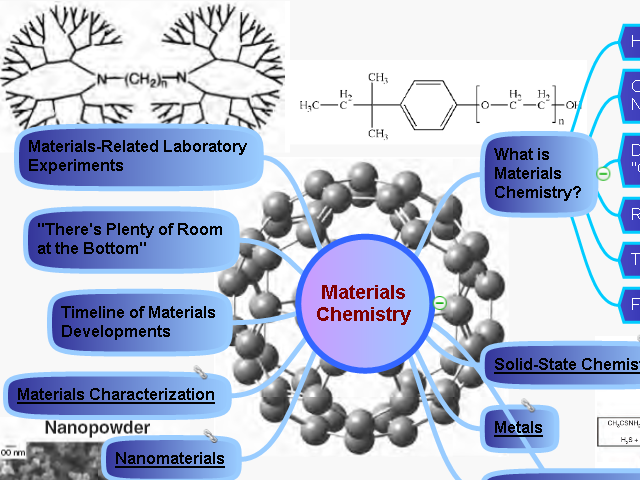
| This is a mind map about Materials Chemistry | |
 | |
| outline | |
| | What is Materials Chemistry? |
| | Considerations in the Design of New Materials |
| | Design of New Materials Through a "Critical Thinking" Approach |
| | Topics for Further Discussion |
| | Materials Characterization |
| | Timeline of Materials Developments |
| | "There's Plenty of Room at the Bottom" |
| | Materials-Related Laboratory Experiments |
| | Amorphous vs. Crystalline Solids |
| | Types of Bonding in Solids |
| | Crystal Growth Techniques |
| | Definitions and Nomenclature |
| | Interstitial Crystal Lattices |
| | Phase-Transformation Diagrams |
| | Physical Properties of Crystals |
| | Crystal Symmetry and Space Groups |
| | Properties Resulting from Crystal Anisotropy |
| | Important Materials Applications I: Fuel Cells |
| | Materials Characterization |
| | Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) |
| | Sample Preparation Techniques |
| | Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopy (STEM) |
| | Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) |
| | Scanning Probe Microscopy (SPM) |
| | Electron Energy-Loss Spectroscopy (EELS) |
| | Sample Considerations and Auger Electron Spectroscopy (AES) |
| | Photoelectron Spectroscopy (PES) |
| | Structure Determination using SEM |
| | Structure Determination using XAFS |
| | Non-Imaging Applications for TEM |
| | Surface Characterization Techniques Based on Ion Bombardment |
| | Bulk Characterization Techniques |
| | Important Materials Applications VI: So Which Acronym Shall I Use? |
| | Mining and Processing of Metals |
| | Metallic Structures and Properties |
| | Phase Behavior of Iron and Iron-Carbon Alloys |
| | Hardening Mechanisms of Steels |
| | Magnetism in Metals, Alloys, and Organometallic Complexes |
| | Non-Ferrous Metals and Alloys |
| | Metal Surface Treatments for Corrosion Resistance |
| | Reversible Hydrogen Storage |
| | Important (and Controversial!) Materials Applications II: Depleted Uranium |
| | Properties and Types of Semiconductors |
| | Silicon-Based Applications |
| | Field-Effect Transistors: Structure and Properties |
| | Integrated Circuit Fabrication |
| | Thin-Film Deposition Methodologies |
| | Light-Emitting Diodes: There is Life Outside of Silicon! |
| | Thermoelectric (TE) Materials |
| | Important Materials Applications III: Photovoltaic (Solar) Cells |
| | Polymer Classifications and Nomenclature |
| | Polymerization Mechanisms |
| | Step-Growth Polymerization |
| | Homogeneous Living Catalysis |
| | "Soft Materials" Applications: Structure vs. Properties |
| | Polymer Additives: Plasticizers and Flame Retardants |
| | Important Materials Applications IV: Self-Healing Polymers |
| | What is "Nanotechnology"? |
| | Nanoscale Building Blocks and Applications |
| | Mechanism for the Nucleation- Growth- Agglomeration of Metal Nanoclusters |
| | The Solution-Phase Synthesis of Nanoparticles |
| | The First 0-D Nanoarchitecture: The Fullerenes |
| | Zero-Dimensional Nanomaterials |
| | Self-Assembly of Nanoparticles- Nanoclusters into Arrays |
| | One-Dimensional Nanostructures |
| | Growth of 1-D Nanostructures |
| | Top-Down Nanotechnology: "Soft Lithography" |
| | Important Materials Applications V: Nanoelectromechanical Systems (NEMS) |
| |