Native Americans of the West: Different Environments, Different Lives |
please flag with care:
| | | 2007-11-19 | No history |  | Add My version | | | Download temporary blocked | | | | This is a sample map from Inspiration 8 software. www.inspiration.com | | 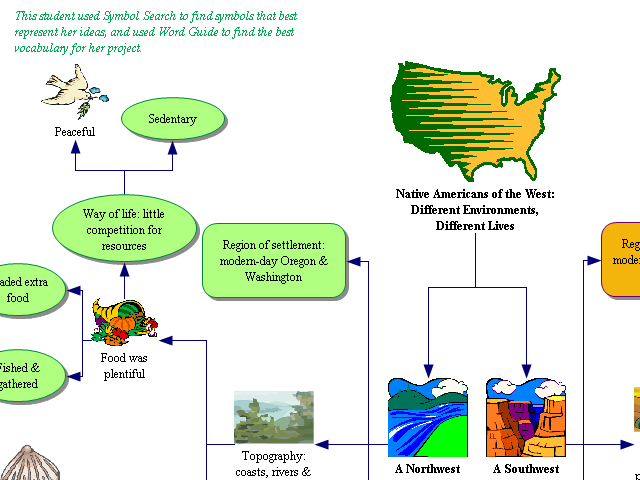 | | | outline | | Native Americans of the West: Different Environments, Different Lives
Different environments led to different ways of life for Native American cultures of the western United States. In comparing two tribes from different western regions—the Chinook and the Navajo—these differences become more apparent.
I. A Northwest culture: the Chinook
A. Region of settlement: modern-day Oregon & Washington
B. Climate: cool and dry summers, wet and mild winters
1. Shelter
a. Wood houses
Some houses were more than 30 metres long.
C. Topography: coasts, rivers & forests
1. Food was plentiful
a. Fished & gathered
An abundance of wild plants and animals exist in the region, so there was no need to raise food by farming.
(1) Fish
Caught and ate many kinds of fish, as well as other seafood. Salmon was a particularly important food source. During salmon runs, one family could catch hundreds of pounds of fish.
(2) Wild plants
Cultures of the Northwest had plenty of plant foods to harvest from the wild.
b. Traded extra food
The Chinook were renowned traders.
c. Way of life: little competition for resources
(1) Sedentary
Tribes could settle in one place without having to look far for food.
(2) Peaceful
The Chinook did not develop a warrior culture. They preferred to solve their differences by staging challenges of skill. Villages of were comprised of mostly relatives, which also made peace more desirable.
2. Crafts
a. Wood plentiful
(1) Canoes
(2) Intricate carvings
b. Carved shells
II. A Southwest culture: the Navajo
A. Region of settlement: modern-day Arizona and New Mexico
B. Climate: hot summers, arid and cold winters
1. Shelter
a. Mud hogans
These were round houses made of wood poles and mud.
C. Topography: mountains, plateaus, prairie & desert
1. Food more scarce
a. Raided settlements for subsistence
The Navajo migrated to the Southwest in the 1400s or 1500s. Before fully adapting to their new lands, the Navajo roamed, raiding to survive. They raided neighbours (including Pueblo towns) for food.
b. Dry-farmed and herded sheep
After adopting farming and herding, many Navajo could sustain their existence without raiding. Some groups of Navajo continued to raid.
c. Way of life: more competition for resources
(1) Raiding
The Navajo raided, even after they settled, during periods of need. Likewise, they were vulnerable to raids from neighbouring tribes and Spanish settlers.
(2) Armed conflict
There was great competition for hunting, herding, and farming ground, especially as populations grew. This brought the Navajo into armed conflict with neighbours, such as the Ute and the local Spanish settlers.
2. Crafts
a. Silver & turquoise jewellery
b. Sand painting
|
| |
|